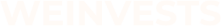In stock trading, risk management is a crucial practice that involves identifying, analyzing, and controlling potential risks associated with trading stocks. By employing robust risk management trading techniques, traders can make informed decisions, maintain discipline, and achieve long-term success in their trading endeavors.
With that being said, beginner traders may have a hard time implementing efficient risk management because of how many tips they can find online related to the subject. It’s not difficult for anyone to get overwhelmed when they try to set up a strategy that involves good risk management.
For this reason, we created this introductory guide. Instead of bombarding you with all sorts of risk management tips, we are going to present you with the key concepts about the matter and get you started with the most important risk management activities that you can implement right away.
In this article, you will learn what risk management is all about, why it’s so important for stock trading, some common types of risks you will deal with when trading stocks, and the key ways to manage risk effectively when trading.
Sounds good? Let’s get started right away then…
What Is Risk Management in Stock Trading?
In stock trading, risk management refers to the process of identifying, analyzing, and controlling potential risks associated with trading stocks or other financial instruments. The primary objective of risk management in stock trading is to protect capital and minimize potential losses while maximizing the potential for gains.
More specifically, risk management concerns itself with:
- Position Sizing
- Stop Loss Orders
- Risk-Reward Ratio
- Monitoring Positions
- Regulating Emotions
In other words, stock traders must determine how much of their portfolios they are willing to risk on a single trade, where they should set stop loss orders according to their theses, what the risk-reward structure looks like to gauge the attractiveness of the trade, and keep monitoring both their positions and their emotions related to them.
Reasons Why Trading Risk Management is Important
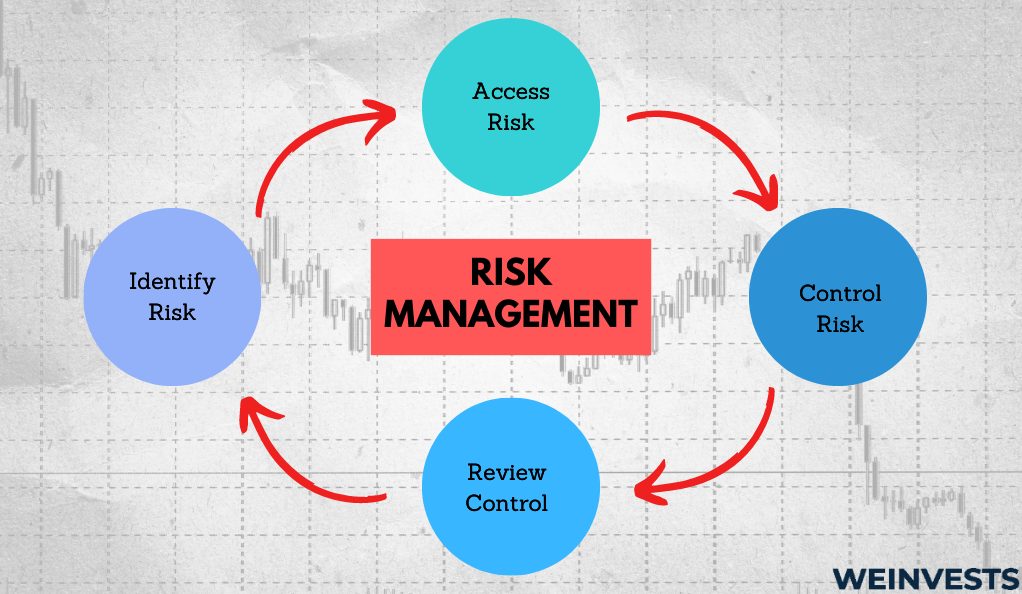
Here are the 3 main reasons why risk management is so important in stock trading:
- Capital Preservation
- Attractive Risk-Reward Structures
- Peace of Mind
Risk management is crucial as it helps stock traders preserve their capital in the long term through the selection of trades with attractive risk-reward structures. What’s not so obvious is that it also helps traders have more peace of mind when it comes to their positions. If you don’t take care to define and regulate the risk you take, this can take a toll on your mental health.
Types of Trading Risks
Before we delve into the steps you need to take to better manage risk in your trading activities, let’s first define the types of risks that exist in stock trading:
- Systematic Risk: Also known as market risk, this is the risk associated with overall market movements. Factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, interest rates, and market sentiment can lead to fluctuations in stock prices, affecting all investments in the market.
- Unsystematic Risk: This type of risk is specific to individual companies and industries. Factors like poor financial performance, management issues, product failures, or legal problems can cause the stock price of a particular company to decline independently of broader market movements.
- Liquidity Risk: This refers to the possibility of not being able to trade a stock quickly at a fair price. Thinly traded stocks can result in wider bid-ask spreads and difficulty trading them efficiently.
- Volatility Risk: This is the potential for large and unpredictable price swings in a stock or the overall market. High volatility can lead to rapid and substantial gains or losses, making it a double-edged sword for traders.
- Currency Risk: If a stock is denominated in a different currency than the investor’s home currency, exchange rate fluctuations can impact the portfolio’s value when converted back into the investor’s currency.
- Interest Rate Risk: Interest rate changes can affect the valuation of certain stocks, especially those of companies in interest rate-sensitive industries like financials and utilities. Rising interest rates can lead to higher borrowing costs, potentially impacting a company’s earnings and stock price.
- Regulatory and Political Risk: Changes in government policies, regulations, or political instability can impact the performance of stocks, particularly in specific industries heavily influenced by government decisions.
- Event Risk: This refers to the uncertainty associated with unexpected events, such as natural disasters, terrorist attacks, or health pandemics. These events can have significant effects on financial markets and individual stocks.
Ways to Manage Risk in Stock Trading
Now that we covered all you needed to know about the concept of risk management and risk types, let us present you with the key approaches to managing risk efficiently:
Diversification

Diversification is the most famous risk principle in investing. The most common definition of diversification has to do with the practice of owning several different assets in a portfolio. However, since this guide is about stock trading, by diversification we refer to owning several stocks of companies operating in different industries and sectors.
By holding a diversified portfolio, traders aim to reduce the impact of individual stock or sector-specific events on their overall investment performance. The key idea behind diversification is that not all stocks will move in the same direction or be affected by the same market forces at the same time. Therefore, when some stocks may experience declines, others may show growth, leading to a more balanced and stable portfolio.
While diversification can’t eliminate all investment risk, it can significantly reduce the impact of adverse events on the overall portfolio, helping traders achieve a more consistent and steady performance over the long term.
Position Sizing
Even if you have a diversified portfolio, you still need to determine how large each stock position will be. Position sizing is the next step in effective risk management and relates to the practice of regulating risk by controlling how much each stock can affect the overall portfolio according to the risk each one carries.
The first step in position sizing is evaluating your risk tolerance and defining the maximum percentage of your portfolio you are willing to risk on a single trade. This risk-per-trade percentage ensures that no single trade has the potential to cause significant damage to your overall portfolio in the event of a loss.
Then consider if volatility is something that matters to you or not. Risk and volatility are not the same things, but many traders choose to take care of each stock’s volatility so the overall returns come out more steady. Highly volatile stocks may require smaller positions to stay within the risk tolerance limits that each trader sets for themselves, while less volatile stocks may allow for larger positions.
Stop-loss Orders
A stop-loss order is a predefined instruction given to a broker to sell a stock when it reaches a specific price level, known as the stop price. The primary purpose of a stop-loss order is to prevent significant losses in case a stock’s price moves in an unfavorable direction.
When a trader places a stop-loss order, they are essentially establishing a point at which they are willing to exit the trade if the stock price moves against their position. By doing so, they can avoid emotional decision-making and eliminate the need to constantly monitor the stock’s price.
The appropriate placement of a stop-loss order is critical, as it should be set at a level that allows the trade to have room to fluctuate without being triggered by minor price movements. At the same time, it should be positioned in a way that helps traders protect a significant portion of their gains if the stock’s price moves against them.
A straightforward way to determine stop-loss orders is to determine the price point below where you bought a stock that will deem your thesis invalid. Some strategies allow for such a thing to be determined and some others do not. So, this kind of thinking is useful in order to avoid setting such orders when they’re not needed.
In conclusion, stop-loss orders can act as a safety net for you but you should develop the ability to know when to use them and when it’s best not to. If you use them for trades that you cannot confidently define the price point or total loss that will prove your thesis wrong, then you might realize losses you don’t have to. At the end of the day, stop-loss orders can restrict how much you lose on a trade but they also realize paper losses.
Profit-Taking
Profit-taking is a crucial strategy in stock trading that involves selling a portion or all of a stock position to realize gains when the stock’s price reaches a predetermined target or satisfactory level. The goal of profit-taking is to secure profits and turn unrealized gains into realized ones before the stock’s price potentially reverses direction.
By setting clear profit targets based on technical analysis, resistance levels, or other indicators, traders can exit their positions when the stock reaches the desired price, protecting their capital from potential downturns.
Profit-taking also helps traders manage their emotions and avoid becoming overly greedy, which can lead to irrational decision-making and increased exposure to market volatility. Integrating profit-taking strategies into their trading plans enables traders to maintain discipline and cultivate a consistent approach to risk management, ultimately contributing to long-term success in the stock market.
Effective profit-taking also plays a vital role in maintaining a well-balanced portfolio and maximizing overall returns. As you sell winning positions to realize gains, you free up capital that can be reinvested in other opportunities or diversified across different assets. This portfolio rebalancing ensures that you are not overly concentrated in a single stock or sector, reducing the overall risk of the portfolio.
Conclusion
In conclusion, efficient risk management trading methods play a very important role in stock trading. Long-term capital preservation, attractive risk-reward structures, and being able to sleep better at night are the greatest benefits that come from implementing risk management techniques.
Getting practical, through diversification, position sizing, stop-loss orders, and profit-taking, traders can control and mitigate the risks associated with trading stocks. Understanding and applying risk management principles allow traders to maintain a balanced and diversified portfolio, navigate market volatility with confidence, and ultimately achieve their financial goals in the dynamic world of stock trading.
However, traders should always take into account that depending on the types of trading they engage in, the specific ways to implement the above concepts will differ. The purpose of this guide was to help you understand the key ideas on risk management and get you started thinking about ways to decrease your risk when trading.
You may now want to consider what the next step in educating yourself about risk management is by examining what your trading style looks like.
FAQ
What is risk management in stock trading?
Risk management in stock trading refers to the process of identifying, analyzing, and controlling potential risks associated with trading stocks.
Why is diversification so important in stock trading?
By holding a diversified portfolio, traders can reduce the impact of individual stock or sector-specific events on their overall investment performance, thus minimizing the risk of significant losses.
What types of risks are involved in stock trading?
Some of the types of risks in stock trading are: systematic risk, unsystematic risk, liquidity risk, volatility risk, currency risk, interest rate risk, regulatory and political risk, and event risk.
WeInvests is a financial portal-based research agency. We do our utmost best to offer reliable and unbiased information about crypto, finance, trading and stocks. However, we do not offer financial advice and users should always carry out their own research.
Read More