Introduction to Cryptocurrency Taxation
Cryptocurrency taxation is of paramount importance in today’s financial landscape. As digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum continue to gain widespread adoption, governments worldwide are grappling with how to regulate and tax these assets effectively.
Understanding cryptocurrency taxation is crucial for individuals and businesses involved in crypto transactions to ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid potential penalties. Moreover, the impact of cryptocurrency on the global economy cannot be ignored, as it presents both opportunities and challenges.
Proper taxation frameworks can help governments harness the economic potential of cryptocurrencies while mitigating risks such as money laundering and tax evasion.
Basics of Cryptocurrency
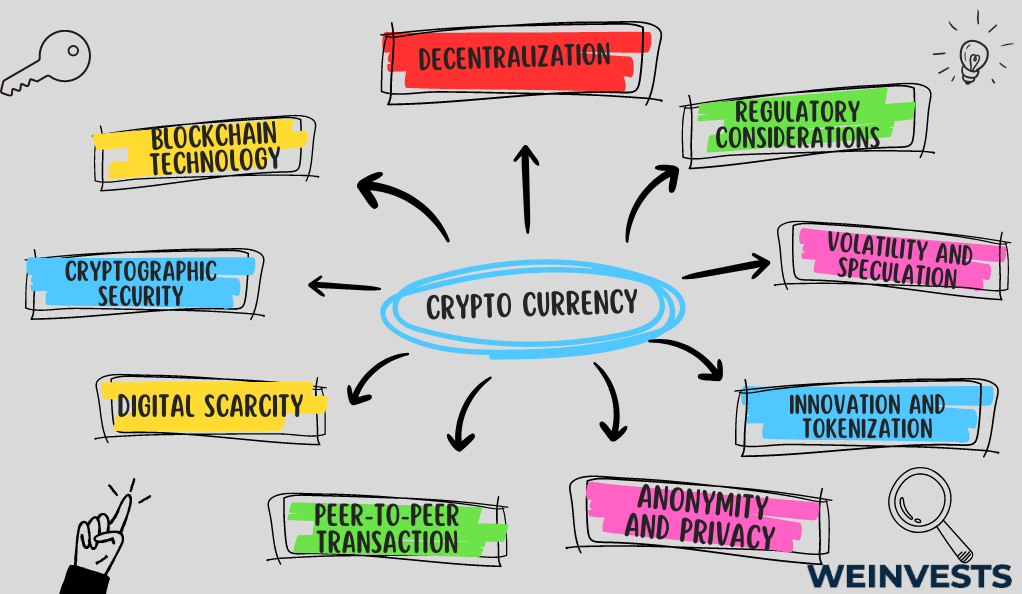
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that utilize cryptography to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. They operate on decentralized networks, typically based on blockchain technology. Here is an overview of the basics of cryptocurrencies:
- Decentralization: Cryptocurrencies are decentralized, meaning they are not controlled by any central authority, such as a government or financial institution.
- Blockchain technology: Cryptocurrencies rely on blockchain, a distributed ledger that maintains a chronological record of all transactions.
- Cryptographic security: Cryptocurrencies employ cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. Public-key cryptography allows users to generate digital signatures to verify transactions, while private keys provide access to their cryptocurrency holdings.
- Digital scarcity: Many cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, have a limited supply. This scarcity is achieved through predetermined rules embedded in the cryptocurrency’s protocol. It ensures that cryptocurrencies cannot be easily manipulated or inflated.
- Peer-to-Peer transactions: Cryptocurrencies enable direct peer-to-peer transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks.
- Anonymity and privacy: While transactions on the blockchain are transparent and can be traced, the identity of users involved in the transactions can remain pseudonymous.
- Innovation and tokenization: Cryptocurrencies have sparked innovation, enabling the creation of programmable digital assets and smart contracts.
- Volatility and speculation: Cryptocurrencies are known for their price volatility, which can present both opportunities and risks for investors. The value of cryptocurrencies can fluctuate significantly due to factors like:
- market demand
- investor sentiment
- regulatory developments
- technological advancements
- Regulatory considerations: As cryptocurrencies have gained popularity, governments, and regulatory bodies have started developing frameworks to address legal and regulatory concerns.
Taxable Events in Cryptocurrency
Taxable events in cryptocurrency refer to specific transactions or activities that trigger tax obligations. It is crucial to identify and understand these events to ensure compliance with tax laws. Here are examples of taxable events in cryptocurrency transactions:
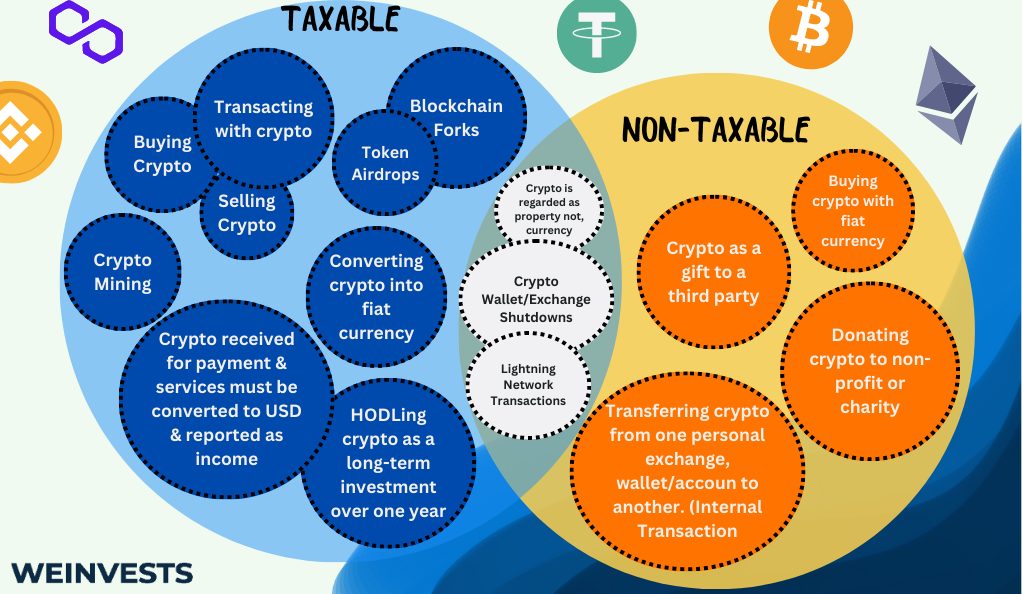
- Buying and selling cryptocurrency:
- Buying cryptocurrency with fiat currency (e.g., USD, EUR) or another cryptocurrency.
- Selling cryptocurrency for fiat currency or another cryptocurrency.
- Exchanging one cryptocurrency for another (crypto-to-crypto transactions).
- Cryptocurrency mining:
- Mining cryptocurrency involves validating and adding transactions to the blockchain. The rewards earned from mining, such as newly minted coins or transaction fees, are typically considered taxable income.
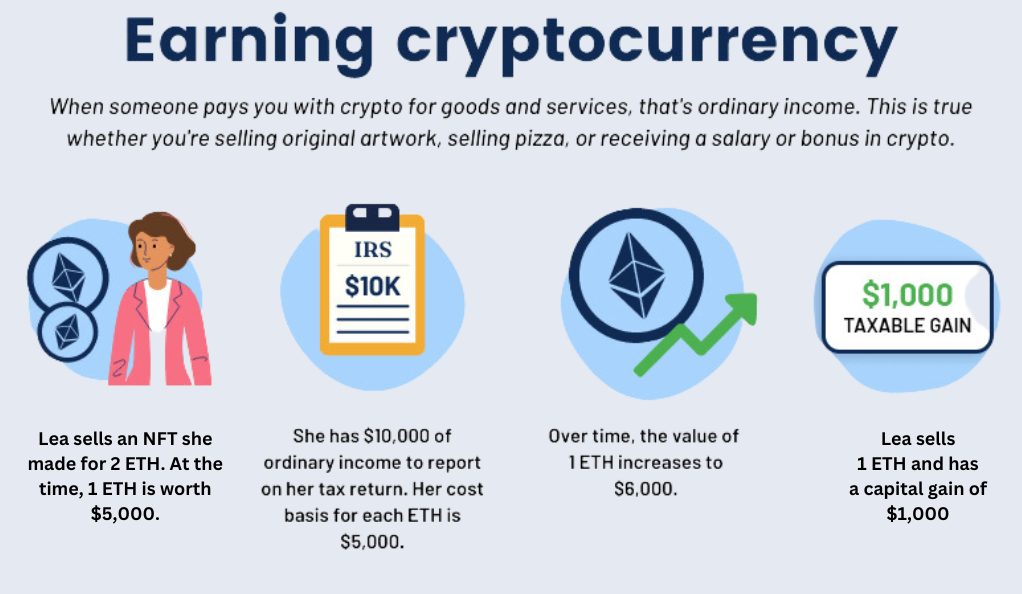
- Receiving cryptocurrency as payment:
- If you receive cryptocurrency as payment for goods or services rendered, it is generally treated as taxable income. The fair market value of the received cryptocurrency at the time of the transaction is used to determine the taxable amount.
- Cryptocurrency airdrops and forks:
- Airdrops occur when a cryptocurrency project distributes free tokens to holders of a specific cryptocurrency.
- Forks happen when a blockchain splits into two separate chains, resulting in the creation of a new cryptocurrency. The newly created coins received from a fork may be subject to taxation.
It’s important to note that tax regulations regarding cryptocurrency can vary across jurisdictions. Some countries may treat cryptocurrencies as property, subjecting them to capital gains tax, while others may consider them as currency or commodities.
Additionally, the holding period, tax rates, and reporting requirements can differ based on individual circumstances and local tax laws. Consulting with a tax professional knowledgeable in cryptocurrency taxation is recommended to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with applicable regulations.
Determining Cryptocurrency Gains and Losses
Let’s have a look at the calculation methods for determining gains and losses in cryptocurrency transactions with the following comparison table:
| Calculation Method | Description |
|---|---|
| FIFO (First-In, First-Out) | Assumes the first cryptocurrency acquired is the first one sold. |
| LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) | Assumes the last cryptocurrency acquired is the first one sold. |
| Specific Identification | Allows taxpayers to select which specific coins to sell. |
It’s important to note that the tax treatment of short-term and long-term capital gains can also impact the calculation of gains and losses. Short-term capital gains occur when assets are held for one year or less, while long-term capital gains apply to assets held for more than one year. Tax rates for long-term capital gains are often lower than those for short-term gains.
Reporting Cryptocurrency Income
When it comes to reporting cryptocurrency income, it is important to fulfill your tax obligations. Taxpayers are generally required to report cryptocurrency income from activities like mining, staking, or receiving cryptocurrency as payment.
This income should be reported on relevant tax returns or specific cryptocurrency-related forms. It is crucial to maintain accurate records of cryptocurrency transactions, including dates and fair market values.
To understand the specific forms and reporting requirements in your jurisdiction, consult your local tax authority or a tax professional. Various tools and software, such as CoinTracking and CryptoTrader.Taxes are available to assist in tracking, calculating, and reporting cryptocurrency income.
Always ensure compliance with local tax laws and seek professional advice if needed to accurately report cryptocurrency income.
Cryptocurrency Taxation Laws and Regulations
Cryptocurrency taxation laws and regulations vary across countries. Here’s a global overview with a focus on key countries:
- United States: The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats cryptocurrencies as property for tax purposes. Cryptocurrency transactions, including buying, selling, and mining, are subject to capital gains tax or income tax.
- United Kingdom: Her Majesty’s Revenue and Customs (HMRC) considers cryptocurrencies as assets subject to capital gains tax. Individuals and businesses are required to report and pay tax on gains made from cryptocurrency transactions.
- Australia: The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) treats cryptocurrencies as assets, and capital gains tax applies when disposing of cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrency used in business transactions may be subject to goods and services tax (GST).
- Canada: The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) treats cryptocurrencies as commodities subject to taxation. Cryptocurrency transactions are subject to income tax or capital gains tax.
- Japan: Japan has recognized cryptocurrencies as legal payment methods. Cryptocurrency gains are subject to taxation, and individuals and businesses are required to report cryptocurrency income to the National Tax Agency (NTA).
Cryptocurrency Tax Strategies
When it comes to cryptocurrency taxation, there are strategies to consider for minimizing tax liabilities and optimizing your financial position. Here are a few key strategies:
- Holding period: Assess your investment goals and consider the potential tax benefits of holding investments for longer periods.
- Tax-advantaged accounts: Explore the use of tax-advantaged accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or Self-Directed Solo 401(k)s, to invest in cryptocurrencies. These accounts provide tax benefits, such as tax-free growth or tax deferral, depending on the account type.
- Tax-loss harvesting: If you have investments that have declined in value, consider selling them to realize capital losses. These losses can be used to offset capital gains from cryptocurrency or other investments, reducing your overall tax liability.
- Specific identification: This strategy allows you to optimize your tax outcomes by selecting coins with a higher cost basis, potentially reducing your taxable gains.
- Gift and donation strategies: In some jurisdictions, donating cryptocurrencies to eligible charities can offer tax deductions based on the fair market value of the donated assets.
- Proper record-keeping: Maintain accurate records of cryptocurrency transactions, including purchase prices, dates, and sale proceeds.
Cryptocurrency Tax Compliance and Penalties
Complying with cryptocurrency tax regulations is crucial to avoid potential consequences and penalties. Non-compliance with tax obligations can result in audits, fines, or legal repercussions. It is important to accurately report cryptocurrency income, calculate gains and losses, and fulfill reporting requirements.
Common pitfalls include underreporting or omitting cryptocurrency transactions, failing to maintain proper records, or incorrectly categorizing transactions.
To avoid these mistakes, seek professional advice, stay informed about local tax laws, and utilize specialized cryptocurrency tax tools or services. Taking proactive measures ensures compliance, minimizes risks, and promotes a transparent and responsible approach to cryptocurrency taxation.
Crypto-to-Crypto Transactions and Taxation
Crypto-to-crypto transactions, where one cryptocurrency is exchanged for another, have tax implications. Such transactions are generally considered taxable events, similar to selling cryptocurrencies for fiat currency.
The fair market value of the acquired cryptocurrency at the time of the trade is used to calculate gains or losses. It is important to accurately track and report these transactions, including dates, values, and associated costs, for tax purposes.
Additionally, depending on the jurisdiction, specific calculation methods may be used to determine gains and losses in crypto-to-crypto trades, such as FIFO, LIFO, or specific identification.
Token Offerings and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs)
Participating in token offerings and Initial Coin Offerings can have tax implications that individuals should be aware of. Here are some key considerations:
- Income tax or capital gains tax: The tax treatment of tokens acquired through ICOs can vary. Some jurisdictions may consider them as income, subjecting them to income tax upon receipt. Others may treat them as assets, resulting in capital gains tax when the tokens are sold or disposed of.
- Reporting requirements: It is important to understand the reporting requirements for tokens acquired through ICOs. You may need to disclose these holdings and any subsequent transactions in your tax returns or specialized cryptocurrency reporting forms.
- Token valuation: Determining the fair market value of tokens acquired through ICOs can be challenging, especially if they are not actively traded on established exchanges. Proper record-keeping and documentation of the acquisition price and valuation methods used are important for accurate tax reporting.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensuring compliance with securities laws and regulations in your jurisdiction is crucial to avoid potential legal consequences.
Summary of Cryptocurrency Taxation Best Practices
Understanding and managing cryptocurrency taxation involves several best practices to ensure compliance and accurate reporting. It is important to familiarize yourself with the tax laws and regulations related to cryptocurrencies in your jurisdiction to fulfill your tax obligations and avoid penalties.
Maintaining accurate records of all cryptocurrency transactions is crucial for calculating gains, losses, and meeting reporting requirements. Seeking professional advice from a tax professional or accountant who specializes in cryptocurrency taxation can provide tailored guidance based on your specific circumstances.
It is essential to stay updated on changes in cryptocurrency tax laws, regulations, and reporting requirements to ensure your tax strategies remain compliant and up to date. By following these best practices, you can navigate the complexities of cryptocurrency taxation, minimize errors, and ensure accurate reporting for tax purposes.
FAQ
What is the definition of cryptocurrency taxation?
Cryptocurrency taxation refers to paying taxes on cryptocurrency transactions.
Do I need to pay taxes on every cryptocurrency transaction?
Taxes are generally required on taxable events involving cryptocurrencies.
How do I calculate gains and losses for cryptocurrency investments?
Calculate gains/losses by subtracting the cost basis from the proceeds.
What are the tax reporting requirements for cryptocurrency income?
Generally, you need to report cryptocurrency income on your tax return, either as capital gains, ordinary income, or self-employment income, depending on the nature of the transaction and your jurisdiction.
How can I minimize tax liabilities on cryptocurrency transactions?
Minimize tax liabilities through strategic planning and timing of transactions.
Are there any tax-advantaged accounts for cryptocurrencies?
Tax-advantaged accounts for cryptocurrencies, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or Self-Directed Solo 401(k)s, may be available in some jurisdictions. These accounts offer potential tax benefits like tax-free growth or tax deferral.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with cryptocurrency tax regulations?
Penalties for non-compliance vary and can include fines, interest, audits, and legal consequences.
WeInvests is a financial portal-based research agency. We do our utmost best to offer reliable and unbiased information about crypto, finance, trading and stocks. However, we do not offer financial advice and users should always carry out their own research.
Read More