This content represents the writer’s opinions and research and is not intended to be taken as financial advice. The information presented is general in nature and may not meet the specific needs of any individual or entity. It is not intended to be relied upon as a professional or financial decision-making tool.
Dividend investing can be very useful for not just retirees, but also investors who can use the extra income while seeing their funds grow.
For this reason, ETFs that invest in dividend-paying companies are a very good choice for the DIY investor who wants broad diversification. Not to mention the benefit of not having to manage your portfolio as actively as directly investing in dividend stocks requires.
In this article, we will outline the 5 best dividend ETFs that retail investors can easily access through a broker.
With that being said, if you have a financial advisor, make sure that you discuss these ETFs with them first before you invest.
Table of Contents
What are ETFs?
For those of you who don’t know yet or need a refreshment, ETFs or Exchange-Traded Funds are investment vehicles structured as stocks listed on stock exchanges.
Investing in one can allow you to indirectly invest in dozens of specific assets or a specific market. They pretty much work just like mutual funds, but with the extra benefit of liquidity and low costs.
You can also view ETFs as companies that invest in various assets that have issued shares for investors like you to buy. And this is what they essentially are. Becoming an owner of an ETF makes you an owner of the assets it owns.
Their assets are basically the underlying securities they hold and that’s why they’re classified as investment vehicles.
Here are a few important concepts you should understand before you go through the following list of the top 5 dividend ETFs:
- Expense Ratio
The annual cost an ETF charges on its assets under management, expressed as a percentage. - Tracking error
The difference between the return of the index the ETF tracks and the ETF’s return. - SEC 30-Day Yield
A yield calculation created by the SEC that measures the yield a fund delivered in the trailing 30 days minus its expenses. - Turnover Ratio
The percentage of assets that were replaced in the ETF’s portfolio.
Top 5 Dividend ETFs
Vanguard High Dividend Yield ETF (VYM)
This ETF was created by Vanguard in 2006 and is tracking the FTSE High Dividend Yield Index. This index measures the performance of stocks with above-average forecast dividend yields.
The most impressive thing about this ETF is its cost. It has an expense ratio of 0.06% as of 02/25/2022, which even by index-tracking ETF standards is very low.
It’s important to also note that in the last 10 years, it had a cumulative market price return of 199.70%. For comparison, the index returned 201.40%, which is not far from the ETF’s performance.
Its 30-day SEC yield as of 12/31/2022 was 2.98%. This is a decent yield but you have to keep in mind that the future annual yield might differ.
In addition, its turnover ratio was at 7.7% as of the fiscal year-end 10/31/2022 which is to be expected from an index fund.
The ETF currently holds 442 stocks in its portfolio with a median market cap of $141.8 billion
This ETF was created by BlackRock in 2011 and tracks the Morningstar Dividend Yield Focus Index which measures the performance of U.S. equities with above-average dividends.
Right now, the fund holds 82 stocks in its portfolio with large exposure to energy, health care, and information technology.
This is a very cost-effective fund with an annual expense ratio of 0.08%.
But it’s also worth paying attention to its cumulative 154.22% market price return in the last decade. The index it tracks returned 157.78%; not far off.
In addition, its 10-year average annual market price return has been 9.78%, while the index’s was at 9.93%. Again, the margin is very narrow.
Schwab U.S. Dividend Equity ETF (SCHD)
This ETF was created by Charles Schwab in 2011 and tracks the Dow Jones U.S. Dividend 100 Index.
Just as expected, its expense ratio is very low at 0.06%, making it a very competitive option for those looking to track the index.
Its assets under management are an impressive $46.78 billion and it has a very high volume of 3,238,942 (shares) as of 1/18/2023.
Its turnover ratio is at 14.99%, which is relatively low for what it’s supposed to do.
When it comes to its trailing twelve-month distribution yield, this is at 3.14% as of 11/30/2022. At the same time, its 30-day SEC yield is at 3.29% 01/12/2023.
As for its returns, in the last 10 years, its average annual market price return was 13.73%. On the other hand, the index returned 13.84% per year during that same period, which is impressively close to the ETF’s performance.
Invesco S&P 500® High Dividend Low Volatility ETF (SPHD)
This ETF was created by Invesco in 2012 and seeks to track the S&P 500 Low Volatility High Dividend Index. The purpose of the index is to measure the performance of 50 securities out of the 500 that the S&P 500 consists of which have returned high dividend yields with low volatility.
Its expense ratio is 0.3%, which is low enough considering the fund’s performance throughout the years.
Its 10-year market price growth has been an average annual of 10.3%. The index it tracks has returned 10.66% over the same period; a small tracking error implied.
Its SEC 30-day yield was 4.22% and its 12-month distribution rate was 3.75%. Probably needless to say now, but the expenses are more than outweighed by its performance and the yield.
Real Estate Select Sector SPDR (XLRE)
This ETF was created by State Street back in 2015 and tracks the Real Estate Select Sector Index.
As the name implies, this index aims to capture the performance of the real estate market as represented by S&P 500 constituents. The ETF, therefore, invests in all the S&P 500 companies engaged in real estate management and development (Equity REITs included).
The expense ratio here is very low for the value the ETF offers at 0.1%. Since its inception, its average annual market price return has been 6.56%. The index it tracks returned 6.70%, instead.
What’s more, its 30-day SEC yield is 3.1% and its distribution yield is 3.45%.
What to Look for Before you Invest in an ETF?
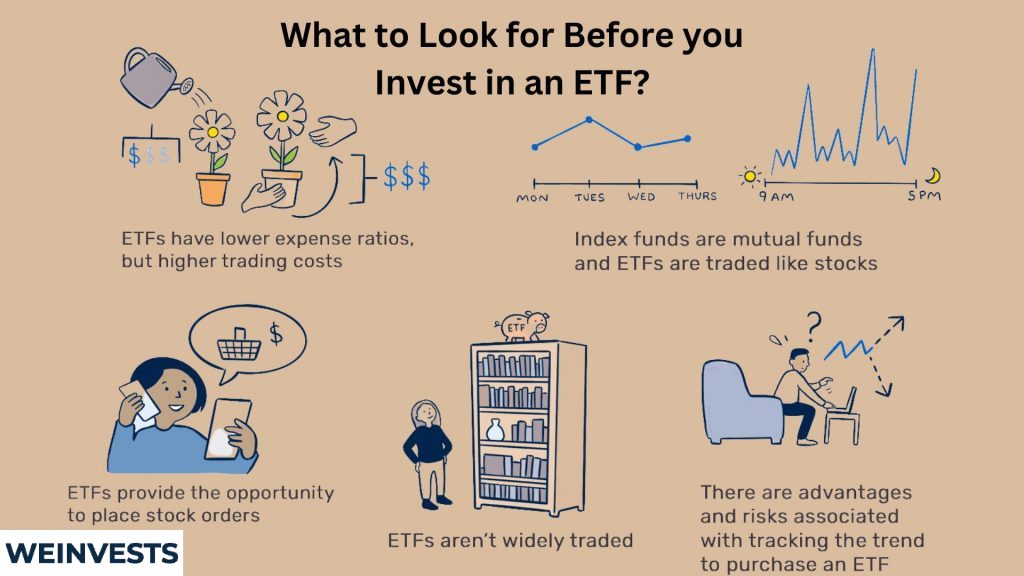
Here are a few things that you should be aware of before you invest in an ETF…
Asset Class
Since there are all kinds of assets that you can think of which ETFs invest in, this is the first thing you should determine.
Some ETFs invest in stocks, others in bonds, derivatives, commodities, or across multiple assets.
Make sure that you have decided what you want the ETF to invest in to narrow down your universe.
Strategy
After you know what assets you want to buy, decide on the strategy based on which the ETF will invest in them.
When it comes to the stock market, for instance, you can choose ETFs that track a stock market index or one that aims to outperform one.
Whatever you go with, confirm that you understand the strategy well before you buy an ETF that employs it.
Expense Ratio
The expense ratio is the annual cost you incur for having your money invested in an ETF and is expressed as a percentage of your invested amount.
ETFs have relatively low expense ratios compared to mutual funds. Still, they can vary widely.
For this reason, after you know what type of ETF you want to buy, seek the one with the lowest expense ratio and move up from there by comparing the following two factors…
Historical Returns
Examining the past returns an ETF has delivered in the past is valuable information. If you know how to use it, of course.
Past returns shouldn’t be used as indicators for the returns you’re going to get. Instead, use this data as a way to assess the superiority of one ETF over another, if both have similar expense ratios.
Turnover
The turnover ratio is the percentage of a fund’s underlying assets that are replaced or “turned over” in a given year.
Generally, the lower the better. The fewer assets are traded, the fewer transaction fees an ETF incurs. Not to mention that capital gains often incur a lower tax rate if an asset is held for longer than one year.
As a rule of thumb, a ~10% turnover is good when it comes to index-tracking ETFs. When it comes to ETFs with a trading strategy, however, a 100% turnover can be excused in some instances; i.e. the fund uses a proprietary trading strategy or has been beating the market for a long time.
What are the Risks Involved with Investing in ETFs?
As with any investment vehicle, there are risks when investing in ETFs. Here are the most significant ones you should be aware of:
Market Risk
This one affects all investment vehicles as it relates to the possibility that the market(s) an ETF invests in will be negatively impacted as a whole.
Bad Management
An ETF’s most important asset is the people that run it. For this reason, when you buy one, you trust that managers will do a good job at realizing the results they aim to achieve. If you’re wrong about the quality of the management, your money is at great risk.
Easy Access
While being able to easily trade ETFs is certainly an advantage as compared to mutual funds, it has a negative side. It can first encourage you to speculate through ETF trading and, second, it gives you access to markets that are not well established yet.
ETF Liquidation
If you invest in an ETF that fails to sell itself in the long term, there’s a chance the managers will shut it down and liquidate the assets. That doesn’t necessarily mean you will end up losing most of your money. It just means that the assets may be sold at unattractive prices, thus incurring some loss.
Where to Buy ETFs From?
If you can buy stocks through your bank or broker, chances are you will be able to also buy ETFs through them.
If not, you can open a brokerage account online and get access to them. TD Ameritrade, Charles Schwab, Interactive Brokers, and Fidelity, all give you such access.
But depending on the countries the ETFs that you’re interested in have been formed, you may not be able to invest in them with a single broker. Determine the list of countries you want to buy ETFs in before you open your account with any broker.
Where to Buy Best Dividend ETFs?
eToro is an excellent option for those looking to invest in the best dividend ETFs. As one of the leading online brokers, eToro has built a solid reputation for offering a wide range of investment options suitable for both beginner and professional traders. In this mini guide, we will walk you through the process of opening an account on eToro to help you start investing in the best dividend ETFs.
Step 1: Open your Personal Account
To begin, navigate to the eToro homepage. From there, click on the “Sign Up” or “Join Now” button to access the registration page. You’ll need to provide some basic personal information, such as your name, email address, and phone number.
Additionally, you’ll be asked to create a unique username and password for your account. Make sure to read and accept the terms and conditions before proceeding. Once you’ve filled in the necessary details, click “Create Account.”

Step 2: Upload ID
After creating your account, you’ll need to verify your identity by uploading a proof of identification. This can be a government-issued ID, passport, or driver’s license. To do this, access the verification section within your account and follow the instructions for uploading a clear, high-resolution image of your chosen ID. Make sure that all required information is visible and legible.
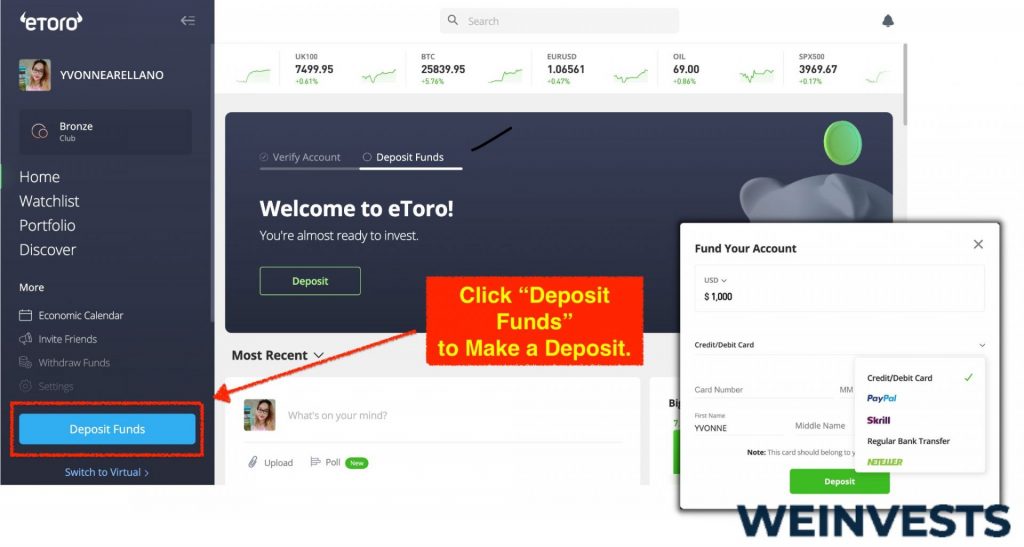
Step 3: Make a Deposit
Before you can start investing, you’ll need to deposit funds into your eToro account. To do this, log in to your account and click on the “Deposit Funds” button. You’ll then be prompted to choose your preferred payment method, such as credit/debit card, PayPal, or bank transfer. Enter the amount you’d like to deposit, and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the transaction.
Step 4: Search for S&P 500 ETFs
Now that your account is funded, you can start searching for the best dividend ETFs on the eToro platform. Use the search bar located at the top of the platform and enter keywords such as “dividend ETFs” or the specific ticker symbol of the ETF you’re interested in. Browse the search results to find the ETF that best suits your investment goals.
Conclusion
Contrary to common belief, it’s not just for retirees. If you’re young and are mainly looking to grow your fund indirectly through market appreciation, dividends are psychologically powerful.
They let you capture some of the returns of a company through cash dividends while you wait for the market to reprice its stock higher. Investors should be patient, but dividends help a lot in this regard.
The problem with dividends is that they’re unpredictable. They may be cut or lowered at any time. An immaculate dividend-paying track record doesn’t guarantee much.
No doubt, the above list of the dividend ETFs are a great selection of some of the more traded dividend ETF’s. They all have a good track record, attractive yields, and fair expense ratios.
Nevertheless, make sure that you discuss these options with your financial advisor before you invest in any of them.
WeInvests is a financial portal-based research agency. We do our utmost best to offer reliable and unbiased information about crypto, finance, trading and stocks. However, we do not offer financial advice and users should always carry out their own research.
Read More