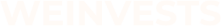This content represents the writer’s opinions and research and is not intended to be taken as financial advice. The information presented is general in nature and may not meet the specific needs of any individual or entity. It is not intended to be relied upon as a professional or financial decision-making tool.
Vanguard has made a name for itself as an investment management company that almost operates as a non-profit. That’s because of its commitment to keep its costs as low as possible in order to deliver the best returns possible to its clients.
But most importantly, it dominates the index investing market through its mutual fund and ETF offerings. Its ETFs, specifically, are cost-effective and unsurprisingly deliver very close market returns to investors.
But if you’re new to its offerings, then you may not understand how to navigate through them.
In this article, we will outline the 5 best Vanguard ETFs that one could trade to limit portfolio volatility.
Note: Remember to always consult your financial advisor before you make any investment decisions as this article does not represent financial advice and should not be interpreted as such.
Table of Contents
What are ETFs?
First, let’s briefly go over what ETFs are.
If you have heard of passive investing, chances are that you have heard of indices.
An index is simply an indicator of financial markets’ performance by tracking the price change (as measured by market capitalization) of such markets.
ETFs, now, are funds that are listed on stock exchanges and have their shares traded just like stocks. You think of an ETF as an investment corporation that manages investors’ money. When you trade an ETF, you indirectly own the assets (stocks, bonds, etc.) that it invests in.
More often than not, they are supposed to follow the returns of indices. So what an index ETF does is hold the constituents of an index in its portfolio and trade them according to any changes the index makes.
Here are a few things to keep in mind regarding ETFs before you continue reading this article:
Expense Ratio
The expense ratio is the annual cost of an ETF or any other fund expressed as a percentage of the assets under management. In the case of Vanguard, however, the expense ratio is charged on the dividends and realized capital gains and not the principal which is the case with most funds.
Tracking error
The tracking error is the difference between the returns of an ETF and those of the index it tracks. The smaller the better.
Turnover
The turnover rate is the percentage of assets an ETF replaced in its portfolio in a given year.
SEC 30-Day Yield
This is the dividend yield as measured in the last 30 days by the SEC minus the expense of the ETF.
Top 5 Vanguard ETFs
Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI)
VTI was created in 2001 and as of 1/20/2023, it had $261.1 billion in assets under management.
Its goal is to track the CRSP US Total Market Index which represents the broad US equity market. Therefore, the ETF includes large, mid, and small-cap stocks in its portfolio. The number of stocks it had as of 1/20/2023 was 3,992.
As with any Vanguard ETF that invests in the US markets, the expense ratio here is a very low 0.03%. This is also one of the reasons for its very narrow tracking error.
Since its inception, the fund has returned an average of 7.52% per year. The index returned 7.53%. The attractive tracking error can also be observed in the last decade’s performance, where it returned an average of 12.08% per year. The index returned 12.09%.
Now, besides the high number of stocks it holds, the ETF’s turnover rate was just 4% as of the fiscal year-end 12/31/2022.
Last, its 30-day SEC yield was 1.65%.
Vanguard FTSE Developed Markets ETF (VEA)
This ETF was created in 2007 and as of January 2023, it was managing about $100.5 billion.
It’s supposed to track the FTSE Developed All Cap ex US Index. As the name of the index suggests, it measures the performance of non-US stocks in developed markets with the classic market capitalization range of small-cap to large-cap.
Its number of stocks as of January 2023, was about 4,062.
Now, regarding expenses, this is a bit pricier because it invests in non-US stocks. But still, the expense ratio is just 0.05%.
Since inception, the ETF returned an average of 1.91% per year, while the index returned 1.8%. In the last 10 years, it returned an average of 4.85%, while the index returned 4.97%.
These returns may not seem much. But they’re to be expected because of the overall performance of a broad range of markets across many countries. Again, this ETF best fits into a portfolio that aims to diversify and decrease overall volatility.
Surprisingly, its turnover rate at the fiscal year-end 12/31/2022 was only 3.1%.
Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO)
The Vanguard S&P 500 ETF was created in 2010 and aims to track the S&P 500 Index which measures the 500 largest companies in the U.S.
As of January 2023, Vanguard has reported that the ETF manages about $262 billion.
Its expense ratio is only 0.03%. Moreso, its performance has been great and its tracking error very low over the years. Since inception, the fund has returned an average annual 12.92% and the index 12.96%.
More recently, its 10-year average annual return was 12.52%, while the index’s was 12.56%.
As for the turnover rate, at fiscal year-end 12/31/2022, it was reported at 2.3%.
Last, its 30-day SEC yield is 1.69%.
Vanguard FTSE Emerging Markets ETF (VWO)
VWO was created back in 2005 and aims to track the performance of the FTSE Emerging Markets All Cap China A Inclusion Index.
The fund has about $68 billion of AUM as of January 2023, and its portfolio consists of stocks from emerging markets all over the world (China, Taiwan, Brazil, South Africa, etc.). A good option for those who want exposure to emerging markets as part of a diversification strategy.
Its number of stocks as of January 2023, was reported at 5,593.
Now, its expense ratio is 0.08%, which is fair considering that operating expenses for Vanguard are usually higher when they invest in non-US markets.
As for performance, the ETF returned an average of 5.16% per year since inception. The index returned 5.31% over that period. Also, its 10-year average annual return was 1.51%, while the index’s was 1.76%.
Last, its turnover rate was at 7.4% for fiscal year-end 10/31/2022.
Vanguard Real Estate ETF (VNQ)
The Vanguard Real Estate ETF was created in 2004 and now manages about $63 billion. Its goal is to track the performance of the MSCI US Investable Market Real Estate 25/50 Index.
This one invests in companies in the Real Estate sector and includes both companies that manage real estate assets and real estate companies that classify as REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts).
It’s a good ETF for anyone who is looking for a combination of decent income and growth.
Its number of stocks as of January 2023, was 167.
The expense ratio of this ETF Is 0.12%. This is great value if you take into consideration the long-term performance.
Since its inception, it has returned an average of 7.43% return per year, while the index returned 7.45%. In the last decade, its return was 6.41%, with the index returning 6.52%.
As for its turnover rate, for fiscal year-end 01/31/2022, it was 7.4%
Last but not least, its TTM yield is a decent 3.72%.
What to Look for Before you buy in an ETF?
Make sure that you go through the following list before you invest in an ETF:
- Asset Class
The first thing you need to consider is the asset class the ETF will invest in. ETFs don’t only invest in stocks, but also bonds, commodities, currencies, derivatives, etc.
- Strategy
Also, examine the ETF’s strategy. Most ETFs may be passively managed, but others try to outperform indices than track them. In any case, understanding an ETF’s approach to investing is very important if you are to invest in it.
- Expense Ratio
The expense ratio is important as it is the annual cost associated with holding an ETF and can impact your returns a lot over time. Most of the time, it’s expressed as a percentage of the AUM.
- Historical Returns
Taking a look at an ETF’s market price returns over the years is very useful. If you’re looking at an index ETF, compare its returns to the index it tracks. They’re usually always lower, but the closer they are to those of the index, the better.
If it’s actively managed, then it should yield better returns than the index it is supposed to outperform. But usually, active ETFs don’t state if they aim to outperform some index. The best you can do here is to use a benchmark such as the S&P 500.
- Turnover
What are the Risks Involved with Investing in ETFs?
The most important risks that come with investing in ETFs are the following:
This risk relates to the potential decrease in market prices. Since most ETFs track indices, they can be directly impacted by a financial crisis.
ETFs have managers, just mutual funds. Though the ETFs that are passively managed cannot be affected by bad investment decisions, there are a lot more things like compliance that can get an ETF in trouble.
The easy access that investors have these days to funds like ETFs makes much more susceptible to trading them and ultimately to speculation.
ETFs can be liquidated for all sorts of reasons. If you have invested in one that goes through that process, you may incur a loss if the assets are sold at attractive prices compared to the cost basis.
Where to Trade ETFs?
You can trade ETFs from any reputable broker or bank.
In case your broker or bank doesn’t provide enough variety, consider opening a brokerage account with Fidelity, Interactive Brokers, Charles Schwab, or TD Ameritrade. All of them have a vast range of offerings when it comes to ETFs.
If you’re a U.S. citizen and are interested in Vanguard ETFs, you can also directly trade from Vanguard. If you’re not a U.S. citizen, you may still be able to do so, but you’ll need to visit this page to check if your country is supported.
Where to Trade ETFs?
Taking advantage of an online broker such as eToro is beneficial when investing in ETFs as it eliminates the requirement of going through multiple platforms to invest and trade the right ETFs. With the onset of the digital era, it has become difficult for investors to make the proper selection of a broker. Thanks to eToro, they can be certain that they will receive top-notch outcomes.
Step 1: Open your Personal Account
To open an account, you’ll need to fill an application form to provide the platform with some personal details, and more information about your investing and trading experience.
Once you complete your application, you’ll be ready to invest in the top ETFs of 2023.

Step 2: Upload ID
This is a document that eToro needs to comply with regulations in terms of KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti Money Laundering).
Documents are required not only to verify your identity but also as proof of residency and proof that you own the bank account you want to use to invest in eToro.
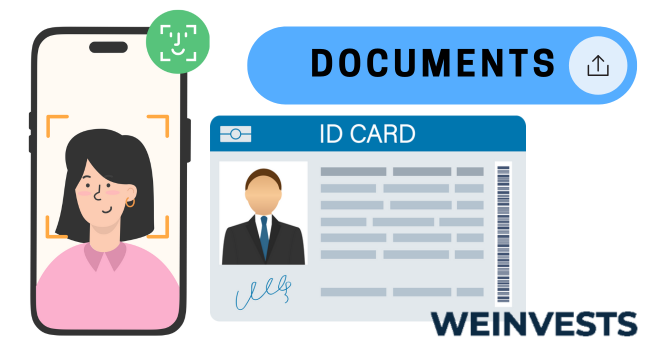
Step 3: Make a Deposit
Even if eToro offers you a virtual wallet to test your trading and investment strategies, you need to deposit money in your real portfolio to have the opportunity to make real profits.
Step 4: Search for ETFs
eToro has a wide selection of ETFs, and if you have something particular in mind, you can use its search bar to find it quickly. After you identify the stock you’re looking for, you can hit the “trade” button to initiate your order. In addition, you can use the available features to determine the stop-loss and take-profit price prices, thereby automating your trading – an important element, if you don’t want emotions to influence your trading activity.
Conclusion
Vanguard surely offers a lot of ETFs and it’s not easy for someone to navigate through them.
The list above cuts through the noise and shows you the 5 best Vanguard ETFs that invest in a variety of markets. If you’re looking to diversify by adding exposure to more markets, you cannot go wrong with the above list.
In any case, it’s always a good idea to ask your financial advisor for their opinion before you invest in any of them.
They will also be able to help you with the matter of asset allocation. Trading ETFs that invest in various markets without understanding how much you should allocate to each one is asking for trouble.
WeInvests is a financial portal-based research agency. We do our utmost best to offer reliable and unbiased information about crypto, finance, trading and stocks. However, we do not offer financial advice and users should always carry out their own research.
Read More