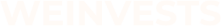In the world of investing, there are various ways to potentially amplify returns and increase the scope of opportunities available to traders. One of them is margin trading.
While it can be a powerful tool to boost profits, margin trading comes with increased risk and requires a thorough understanding before diving in. Even professional traders lose a lot of money when trading on margin. It’s not just for experienced traders, but for those who meticulously manage risk when they approach margin trading.
If you’re a beginner, margin trading is probably not for you. But all traders who use margin have started from somewhere, so an article that covers the basics of margin trading would be useful. That’s where we come in. We wanted to create a comprehensive introduction to margin trading for beginners, covering the basics, benefits, risks, and more.
However, it’s best to use the knowledge you are going to gain here to experiment with paper trading instead of real money. The thing is that you are going to make mistakes no matter how well-prepared you are. But as opposed to when you just trade with your own money, mistakes in margin trading can get you in great trouble. It’s best to make these initial and often costly mistakes with a simulator. Many brokers provide one and there is a chance you can find an even better one in apps or websites.
Having said that, also make sure to thoroughly read the section regarding the risks of margin trading later in this article.
What is Margin Trading?
Margin trading is a method of trading that allows investors to borrow funds from a brokerage or exchange to increase their buying power beyond their available capital. In essence, it enables traders to leverage their positions, magnifying potential gains but also intensifying potential losses. This type of trading is not limited to stocks; it is prevalent in various financial markets, including the forex market, commodities, and cryptocurrencies, among others.
To participate in margin trading, traders must open a margin account with a brokerage firm. This account permits borrowing funds, using the existing holdings or assets as collateral. The amount of borrowed money is referred to as margin, and the trader’s own contribution is the margin requirement or equity.
The practice of buying securities on credit and borrowing money to invest in the stock market can be traced back to the 19th century. However, margin trading as we know it today, with specific rules and regulations, started to take shape in the early 20th century. The practice of borrowing money to invest in the stock market gained popularity in the 1920s during the “Roaring Twenties” in the United States. This period saw significant speculation in the stock market, fueled by easy credit and a booming economy.
In response to the market crash and the ensuing financial crisis, the U.S. government introduced the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. These acts brought significant changes to the regulation of margin trading and aimed to protect investors from excessive risk-taking.
Nonetheless, traders are still at great risk when trading on margin and no amount of regulation will protect their assets as well as efficient risk management.
Understanding Margin Trading
To understand margin trading, it’s best to illustrate the concept through a simple example.
Let’s suppose that you want to buy 100 shares of a stock at $50 per share. The cost would be $5,000. However, let’s say you only got $2,500 available to invest, half of the required amount for the 100 shares. With access to a margin account, you could get a 2:1 leverage, allowing you to borrow $2,500 from your broker and buy the number of shares you want.
If the stock price increases to $60 per share after you buy on margin, you will have made 40% on your equity capital ($1,000 gain on $2,500 of equity). If you bought the stock without margin, your return would be 20%, half what you would get with buying on margin.
By the same token, if the stock price falls to $40, your loss would be 40%. By only buying the stock with your own money, you would only incur a 20% loss. As you can see, buying on margin can also magnify losses.
To make the above example simple, we avoided talking about interest expenses. However, you should always consider the fact that in practice your returns will not be as great and the losses won’t be as small as in theory if you account for the interest you pay your broker to trade on margin.
The Benefits of Margin Trading
Margin trading offers several benefits that attract investors and traders seeking to capitalize on market opportunities. Let’s examine a few of them…
Increased Buying Power
The primary advantage of margin trading is the ability to access a larger pool of funds than what the trader initially possesses. This expanded buying power allows them to take advantage of potential profit opportunities they might have otherwise missed due to capital constraints.
Leveraged Profits
With margin trading, traders can amplify their gains when successful. The ability to control a more substantial position with less capital invested means that profits are magnified. However, this is a double-edged sword, as it also magnifies losses in the event of unfavorable price movements.
Access to Ongoing Credit
Margin loans offer a readily accessible credit source without the need for approval or credit checks typically required by banks. Additionally, there is no strict repayment schedule as long as the minimum required equity is maintained in the trading account.
In situations where short-term cash flow needs arise, opting for a margin loan and paying interest can serve as a convenient alternative to liquidating a portion of one’s investment portfolio. By doing so, investors can avoid locking in potential capital gains and the subsequent tax implications that come with such liquidation.
The Risks of Margin Trading
While margin trading offers the potential for higher returns, it comes with significant risks that traders must be aware of before participating. Let’s look at some of them…
Increased Losses
Just as margin trading can multiply profits, it can also amplify losses. If a trade moves against a trader’s position, the losses will be larger than if they had used only their own capital.
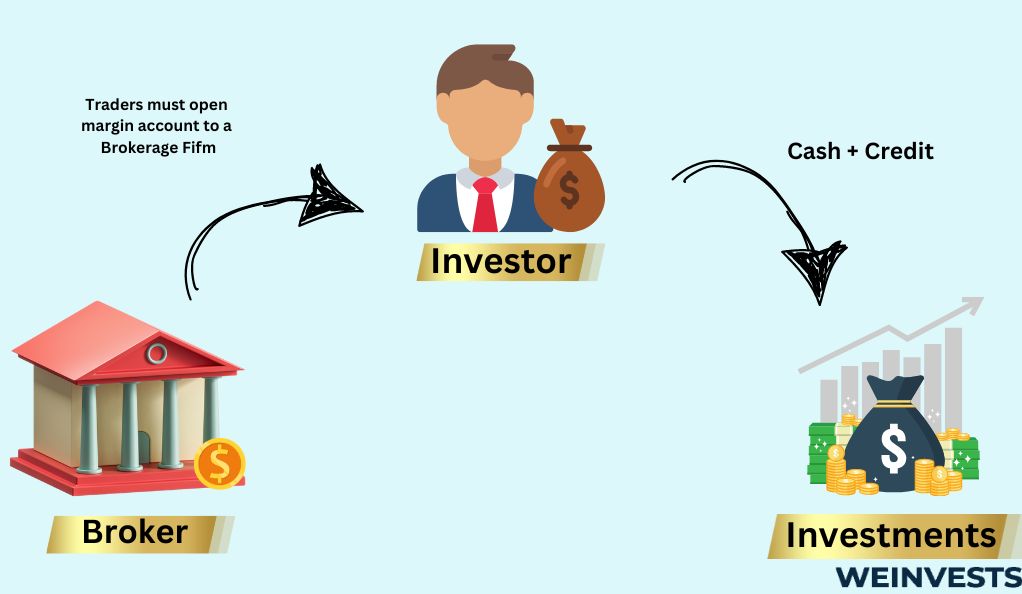
Margin Calls
One of the most critical risks in margin trading is the possibility of a margin call. A margin call occurs when the account’s equity falls below a certain threshold set by the brokerage. When this happens, the trader must either deposit additional funds or close positions to restore the required equity level. Failing to meet a margin call could result in the brokerage liquidating the trader’s assets to cover the losses, potentially leading to a substantial loss of capital.
Volatility
Volatility is the degree of fluctuation or variability in the price of a financial asset. While volatility isn’t necessarily a risk for some traders, it can result in paper losses that may cause great discomfort. But even worse, it can also cause a margin call, which we talked about above.
As you can imagine, margin trading will amplify the effect of volatility on the equity part of your investment. Sudden and sharp price movements can lead to significant losses, especially if a trader is highly leveraged.
Margin Trading Tips
Before engaging in margin trading, it is essential for beginners to have a well-defined strategy and risk management plan in place. Here are some tips for beginners:
Proper Research and Analysis
Thorough research and analysis are fundamental to any trading strategy, but it becomes even more critical in margin trading. Traders must assess the potential risks and rewards of each trade and ensure they have a strong understanding of the market and the asset they are trading.
Whether you’re a day trader or value investor, it’s probably best to conduct thorough due diligence and carefully examine your thesis before you seek to amplify returns through margin trading.
Setting Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are essential risk management tools for margin traders. These orders automatically close a position when the asset’s price reaches a certain predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
Limiting Leverage
While high leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the likelihood of margin calls and significant losses. If you’re a beginner, you may want to start with conservative leverage and gradually increase it as you gain experience and confidence.
Conclusion
Margin trading can be a powerful tool for experienced and knowledgeable traders, but it comes with substantial risks that beginners must thoroughly understand before venturing into this territory.
No doubt, this approach to trading offers increased buying power, leveraged profits, and a superior way to trading with borrowed funds, but it also exposes traders to amplified losses, margin calls, and increased costs.
To succeed in margin trading, one must combine proper research, risk management strategies, and continuous learning to navigate the dynamic and challenging world of leveraged trading. Always remember that informed and prudent decisions are the cornerstones of successful margin trading.
As with any form of trading, practice, education, and patience are vital elements of a trader’s journey. Beginners should seek to grow their knowledge, gain experience with small positions, and gradually increase their involvement in margin trading as they become more confident in their abilities.
FAQ
What is margin trading, and how does it work?
Margin trading is a method that allows investors to borrow funds from a brokerage or exchange to increase their buying power beyond their available capital. It enables traders to leverage their positions, amplifying potential gains but also the potential losses. Traders must open a margin account with a brokerage, using their existing holdings or assets as collateral. The borrowed money is referred to as margin, and the trader’s contribution is the margin requirement or equity.
What are the benefits of margin trading?
Margin trading offers several benefits, including increased buying power, leveraged profits, and access to ongoing credit. It allows traders to participate in larger trades, capitalize on potential profit opportunities, and provide an alternative to liquidating part of their portfolio for short-term cash flow needs.
What are the risks associated with margin trading?
While margin trading can magnify profits, it also amplifies losses. One critical risk is the possibility of a margin call, where the trader must deposit additional funds or close positions to restore the required equity level. Volatility in the market can also lead to significant losses, especially if a trader is highly leveraged.
Is margin trading suitable for beginners?
Margin trading is not recommended for beginners due to the increased risk involved. It requires a thorough understanding of the market, risk management, and a well-defined trading strategy. Beginners are encouraged to gain experience through paper trading or simulator platforms before risking real money with margin trading.
What are some tips that beginners should follow before they try trading on margin?
For beginners interested in margin trading, proper research and analysis are essential. Traders must conduct due diligence and understand the market and assets they trade. Setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and limiting leverage are also very important when getting started. On top of these, it’s a good idea to start with conservative leverage and gradually increase it as you gain experience and confidence.
WeInvests is a financial portal-based research agency. We do our utmost best to offer reliable and unbiased information about crypto, finance, trading and stocks. However, we do not offer financial advice and users should always carry out their own research.
Read More