Finance has long been at the forefront of technological innovation.
The rise of the telegraph in the 19th century led to the expansion of banking.
Meanwhile, the invention of the Internet in the 20th century helped launch electronic trading and markets, reducing the need to transfer physical securities.
In the 21st century, the latest generation-defining technology is artificial intelligence (AI). AI is powered by machine learning, which involves training computers and programs to improve performance on certain tasks over time.
In line with history, the financial industry has been eager to adopt AI in order to improve profit margins and beat out the competition.
In this article, we’ll cover the basics of how AI works today, and review the ways in which the technology is being put to work on a wide array of tasks within the financial industry.
Table of Contents
The Recent Growth in AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence isn’t exactly a new idea. Back in the 1940s, computer science pioneer Alan Turing had already developed the idea of training machines to think like humans.

But it would take a long time before machine learning algorithms had improved enough to actually real artificial intelligence.
A recent expansion in the power of machine learning algorithms is largely responsible for the stunning gains in AI we’ve seen recently.
New algorithms
Today, the most popular style of machine learning algorithms (which power tools like ChatGPT) are neural networks.
Neural networks mimic the way the brain works, building a string of digital synapses and connections that activate based on the strength of some underlying data.
They are highly complex, requiring advanced mathematics to decipher. But they are also incredibly powerful and are being used to successfully train computers to identify images, speak languages, and even generate original content.
Aside from neural networks, other popular machine learning algorithms include gradient boosted machines, support vector machines, and hidden Markov models.
But it’s not just the explosion in algorithmic complexity that’s driven AI forward in recent years.
Growth in data
Machines require an enormous amount of data to effectively learn.
In the past, there just wasn’t enough data on hand to train computers properly. Even if you could assemble enough data in the form of images, text, or video, such data was very expensive to store.
But as the internet and computing have taken over our world, the amount of data generated has increased tremendously. Based on one estimate, the amount of data stored worldwide grew 13 times in the past decade.
Think of data as the “raw material” that algorithms need in order to create AI.
As data generation has exploded globally and the cost of holding onto all that data has plummeted, it’s no surprise that algorithms are getting ever more proficient at creating groundbreaking AI.
In fact, one of the reasons AI is so prevalent in finance is due to the wealth of trading and market data available.
Algorithmic Trading
AI is proving to be a huge asset for algorithmic traders.
Algorithmic trading involves outsourcing investment decisions to a computer. Typically, this trading is done on a high-frequency basis, taking advantage of small discrepancies in price to turn a profit.
Think of the way a human trader works – they interpret current market data based on past experience in order to enter a series of trades designed to make money.
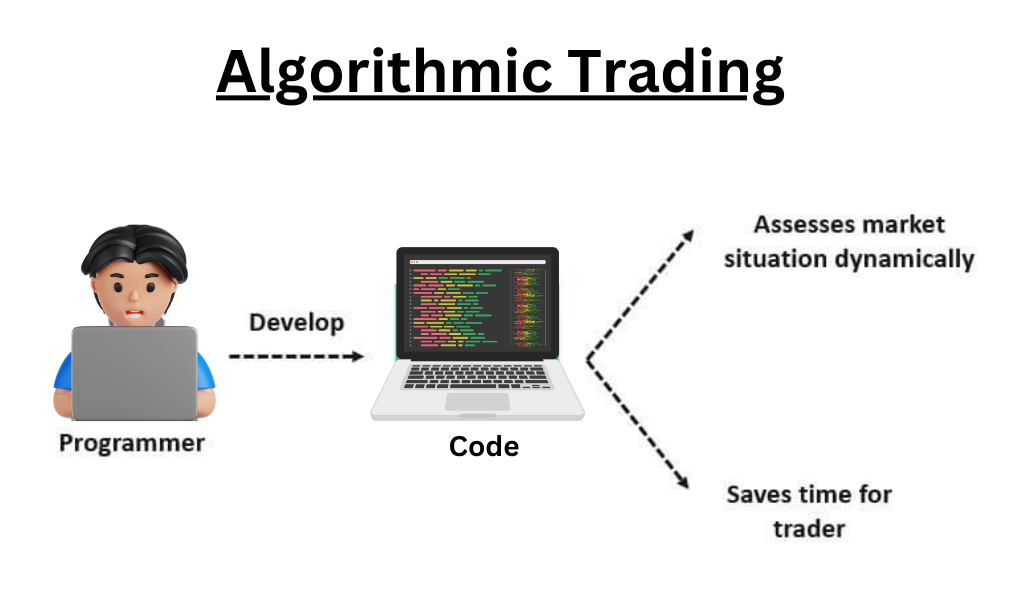
AI can work in much the same way, using machine learning techniques to learn from market data – but at a significantly more rapid pace.
In fact, some secretive firms have long used AI to get a leg up on the rest of the market. Renaissance Technologies, a Long Island-based hedge fund, has used machine learning to generate post-fee returns of more than 39% annually since 1988.
As research has caught up, though, more and more firms are leveraging AI to improve returns.
Not all AI trading strategies rely on tools as complicated as neural networks – but these days, algorithmic trading is increasingly dominated by some form of AI.
But with the high rewards of algorithmic trading come high risks. Famously, Knight Capital lost approximately $440 million in 2012 when a computer trading system failed.
As algorithmic trading strategies continue to leverage AI in order to improve returns, they’ll need to ensure their risk management systems keep pace.
In fact, some areas of finance are using AI itself as a cutting-edge risk management tool.
Credit Scoring
One of the biggest ways lenders determine whether to extend credit to people or not is based on their credit score.
Your credit score is that important three-digit number that is calculated based on factors like your credit utilization, your credit mix, and your payment history.
If your credit score is too low, you’ll probably find yourself with limited opportunities to borrow money.
Credit scores are useful to lenders since they quickly summarize important information about a potential borrower. But they’re also very crude measures and don’t always capture critical information.
AI is being used to overcome some of the limitations of traditional credit scoring. By training a set of algorithms based on historical data, AI can come up with a potentially more accurate judgment of risk.
According to Experian, one of the big three credit bureaus, limitations of traditional credit scoring include:
- Slow reaction times: Traditional credit risk models can take months to build and deploy
- Fewer data sources: Traditional models may struggle to incorporate certain data points
- Less effective performance: Research indicates that lenders experience a 25% reduction in exposure to risky borrowers when using AI
Considering these drawbacks, it’s no surprise lenders are increasingly considering using AI to replace or supplement traditional credit scoring.
However, some critics are pushing back against the use of AI to determine who should get credit and who shouldn’t.
Remember how we said that machine learning algorithms are getting more complex? Well, one of the problems with that is that it’s increasingly difficult to explain what AI is up to.
If an AI rejects a borrower for credit, it could be for some justifiable reason. But it’s also possible that a borrower was rejected due to their race, sexuality, or some other bias hidden in the algorithm.
With no way to ask AI how it makes such decisions, it’s almost impossible for people to determine whether the system is operating fairly.
Clearly, the implementation of AI isn’t just a technical one – it also comes with moral and ethical implications we need to be aware of.
Fraud Detection
In the last section, we saw how AI is being used to improve credit risk measurement for lending organizations.
Increasingly, AI is also being used to protect against another kind of risk – fraud.
The modern financial system is truly massive. In 2019, there were more than 100 million transactions in the United States every single day – just with credit cards.
Add in all the other types of payment methods, and you’ll understand just how much money gets transferred every day.
Given all those transfers and payments, there’s bound to be some fraudulent behavior going on. But detecting it is enormously difficult, especially as fraudsters work to combat the banks and regulators trying to catch them.
With AI, financial institutions can make the job of detecting fraud a little easier. Given all the transfers that go on every day, there’s an enormous amount of data on what legitimate and non-legitimate transactions look like.
By feeding all that data to machine learning algorithms, AI can be trained to flag suspicious transactions for further review.
Have you ever had a credit card payment denied, only for your provider to call you and ask if you indeed tried to make that purchase?
It’s possible the payment was outside your standard pattern of behavior, and an AI system thought it was suspicious.
But just as AI is being used to detect fraud, AI is also allowing scammers to supercharge their operations.
Recent reports indicate fraudsters are using AI tools to replicate people’s voices, only to call their loved ones and ask for money.
This example helps show that, despite how impressive the technology is, the rise of AI in finance may end up being a mixed blessing.
Content Creation
The final area in which the financial industry is leveraging AI is in content creation – specifically, creating financial news articles, research reports, analyst commentary, investor communications, and more.
With the rise of generative AI, businesses can create written content at the push of a button.
Often, that content is criticized for being repetitive and formulaic.
But for the financial industry, those traits aren’t as big of a drawback as they might be elsewhere.
Oftentimes, press releases or investment research are designed to communicate facts and figures. So formulaic writing isn’t exactly a bad thing.
Financial advisors, who frequently have to generate client communications, are one of the roles benefiting the most from AI in the industry.
In fact, this use of AI is so popular in finance that specific tools are being built to improve the content quality for financial practitioners.
Daizy is a plugin for ChatGPT that highlights its data accuracy. Writer, meanwhile, is being used by companies like Vanguard.
Increasingly, companies are building in-house tools for their employees to use. Morgan Stanley recently unveiled an AI assistant for its advisors, which can draw upon the firm’s wealth of research documents to craft client communications.
As the use of AI in finance continues to evolve, expect other firms to start debuting proprietary tools, designed to craft compliant, accurate writing that aligns with brand voice.
Conclusion
In the future, expect to see an even deeper integration of AI into the financial industry.
For instance, we may see an expansion of AI tools designed to help individuals manage their portfolios or personal finances.
Brokerages may also supply AI assistants to customers to help them make trading decisions.
AI tools are certainly impressive, and the technological advancements they embody represent a major step forward in machine intelligence and algorithmic complexity.
But such tools should also be used cautiously. We saw how trading errors can quickly multiply when computers are involved.
Moreover, generative AI frequently hallucinates incorrect or misleading facts, requiring human oversight before any such communication is sent to a client
Finally, as certain fraud examples show, not everyone using AI these days is doing so responsibly. As financial institutions use AI to monitor threats and risks, fraudsters will no doubt leverage the same tools to try and beat such systems.
The future of AI in the financial industry is exciting, if uncertain. One thing is for sure, though – the industry as a whole will continue to embrace cutting-edge technology in order to generate profits, improve returns, and stay one step ahead of the competition.
FAQ
How is AI being used in finance?
AI is being used in finance in a number of different ways. First, it’s being used as a source of alpha for algorithmic trading strategies, as new machine learning algorithms introduce innovative ways to understand market data. Next, it’s being used to better calculate both credit risk and fraud risk. Finally, it’s being used to generate written content for financial professionals. In the future, the use of AI in finance is likely to expand.
Is financial industry at risk of AI?
Overall, some jobs in the financial industry may be at risk of AI. Customer service representatives, for instance, may be replaced in some cases with virtual AI assistants. Marketing professionals, as well, may see demand for human-written content decline. But at the current stage of the technology, AI is not yet advanced enough to replace the vast majority of industry jobs.
What is algorithmic trading?
Algorithmic trading is a deep, complicated topic that combines mathematics, computer science, financial engineering, and other fields. Broadly speaking, the goal of algorithmic trading is to delegate investment decisions to a computer, which performs analysis in order to profitably execute trades.
Why is AI the future of finance?
It’s hard to say whether AI is the future of finance. While the tool is certainly being used in diverse contexts within the industry, there are plenty of compliance concerns associated with its use. While it’s likely that AI will continue to be an important tool for the industry, it’s also possible that regulatory restrictions come into play.
WeInvests is a financial portal-based research agency. We do our utmost best to offer reliable and unbiased information about crypto, finance, trading and stocks. However, we do not offer financial advice and users should always carry out their own research.
Read More